Quite frankly, I no longer care if AGW makes this planet uninhabitable. If humanity allows Israel to commit a Genocide in broad daylight, it does not deserve this planet. https://x.com/R34lB0rg/status/1875088107168567440
Destruction of Essential Resources: Eight members of the Israeli Parliament Foreign and Defense Committee demanded the destruction of all energy sources, food sources, and the imposition of a siege in Gaza, which aligns with the act of "imposing living conditions intended to destroy" a group as defined by the UN Genocide Convention. This is supported by the statement in the post that calls for the destruction of all sources of water, food, and energy in northern Gaza, aiming to ensure Hamas' defeat but effectively targeting the civilian population's survival needs.
Forced Transfer and Siege: The call to "lay siege and remotely kill everyone not flying a white flag of surrender" suggests an intent to forcibly transfer or eliminate those who do not comply, which could be interpreted as genocidal intent under the acts of "forcibly transferring" and potentially "killing members of the group." This is echoed in the related web results where similar calls for sieges and forced displacement have been made, indicating a pattern of behavior.
Public Statements of High-Ranking Officials: Statements from Israeli officials have been characterized as expressing genocidal intent. For example, Yoav Gallant's announcement of a "complete siege" of Gaza with plans to cut off vital supplies has been flagged as potentially genocidal. Similarly, the post mentions parliamentarians calling for war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide, and aggression, which is consistent with the narrative provided in the web results.
Dehumanizing Language: The use of phrases like "fighting human animals" by Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, as noted in the web results, indicates dehumanization, which is often a precursor to genocidal acts. This rhetoric fosters an environment where the destruction of a group becomes more acceptable.
Intent to Destroy: The post and the web results mention explicit calls for actions that could lead to the destruction of the Palestinian population in Gaza, such as "total annihilation" and the use of extreme measures like nuclear weapons or "doomsday weapons." These statements align with the intent to destroy a group in whole or in part, a key element of genocide.
Legal and Scholarly Analysis: Scholars and legal experts have analyzed these actions and statements as potentially meeting the criteria for genocide. For instance, Mark Levene and others have argued that Israel's actions in Gaza could constitute genocide based on the intent to ethnically cleanse or destroy the Palestinian population. This scholarly perspective is reflected in the web results.
This analysis is based on the content of the X post and the related web results, providing a broad spectrum of evidence suggesting genocidal intent according to international legal standards and scholarly interpretations.

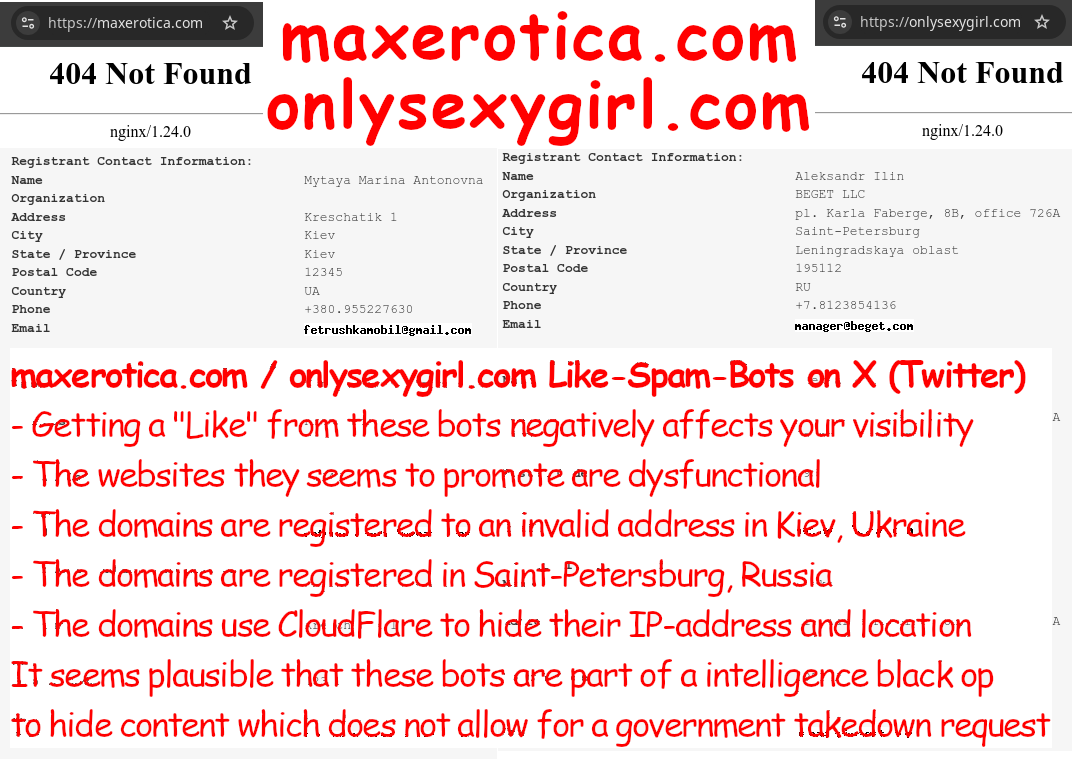
Every time a posting mentions G_E_N_O_C_I_D_E, the spambots like it so that the X algorithms know to hide it....
Reasonable to assume that these bots are part of a Israeli / Hasbara / Mossad black op. https://x.com/R34lB0rg/status/1875063355188388349/photo/1
Based on the content of the X post you've indicated (1874845322259709981) and the associated web results, here's a summary of the evidence for genocidal intent:
Destruction of Essential Resources: Eight members of the Israeli Parliament Foreign and Defense Committee demanded the destruction of all energy sources, food sources, and the imposition of a siege in Gaza, which aligns with the act of "imposing living conditions intended to destroy" a group as defined by the UN Genocide Convention. This is supported by the statement in the post that calls for the destruction of all sources of water, food, and energy in northern Gaza, aiming to ensure Hamas' defeat but effectively targeting the civilian population's survival needs. This is cited in ``.](https://www.middleeasteye.net/news/how-amnesty-international-concluded-israel-has-genocidal-intent-gaza))
Forced Transfer and Siege: The call to "lay siege and remotely kill everyone not flying a white flag of surrender" suggests an intent to forcibly transfer or eliminate those who do not comply, which could be interpreted as genocidal intent under the acts of "forcibly transferring" and potentially "killing members of the group." This is echoed in the related web results where similar calls for sieges and forced displacement have been made, indicating a pattern of behavior.
Public Statements of High-Ranking Officials: Statements from Israeli officials have been characterized as expressing genocidal intent. For example, Yoav Gallant's announcement of a "complete siege" of Gaza with plans to cut off vital supplies has been flagged as potentially genocidal. Similarly, the post mentions parliamentarians calling for war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide, and aggression, which is consistent with the narrative provided in the web results.
Dehumanizing Language: The use of phrases like "fighting human animals" by Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, as noted in the web results, indicates dehumanization, which is often a precursor to genocidal acts. This rhetoric fosters an environment where the destruction of a group becomes more acceptable.
Intent to Destroy: The post and the web results mention explicit calls for actions that could lead to the destruction of the Palestinian population in Gaza, such as "total annihilation" and the use of extreme measures like nuclear weapons or "doomsday weapons." These statements align with the intent to destroy a group in whole or in part, a key element of genocide.
Legal and Scholarly Analysis: Scholars and legal experts have analyzed these actions and statements as potentially meeting the criteria for genocide. For instance, Mark Levene and others have argued that Israel's actions in Gaza could constitute genocide based on the intent to ethnically cleanse or destroy the Palestinian population. This scholarly perspective is reflected in the web results.
This analysis is based on the content of the X post and the related web results, providing a broad spectrum of evidence suggesting genocidal intent according to international legal standards and scholarly interpretations.

Humanitarian organization are forced to hand over the aid deliveries to Israel at the crossings into Gaza for the goods to reappear on the markets in Gaza for a heavy price.
I am formally accusing Israel of 1.) Blocking humanitarian access 2.) Using starvation as a weapon 3.) Selling aid to the people in Gaza

What is happening in Gaza City is not just a bombing, but a genocide being committed before the eyes of the world. The occupation aircraft have turned the city into an open target, as they have targeted 23 separate airstrikes since this morning until this moment, resulting in the martyrdom of 39 citizens. As Gaza City teems with displaced people, every Gazan becomes a potential target, and every bomb that falls represents a new crime. Gaza is now living moments of pain and oppression under merciless fire.
The vilest savages who ever walked the earth. Their atrocities are so heinous that even Lucifer himself blanches and recoils in disgust. 💔😭🇵🇸 https://x.com/HossamShabat/status/1874602455079776601
A number of injuries arrived at Nasser Hospital as a result of the occupation aircraft targeting the tents of the displaced in Mawasi Khan Yunis https://x.com/HossamShabat/status/1874602455079776601
US is supplying Israel with its military power to genocide Gaza and attack Iran, Lebanon, Syria and Yemen but Russia must follow international law. 🤡🌍 https://x.com/World_Affairs11/status/1874525322869350568